
![]()
Announcement
02/2026
Daikin Industries, Ltd.× The University of Osaka
Proposing an innovative new electrolyte design approach for lithium-ion batteries
~Contributing to the increased voltage and safety enhancement of lithium-ion batteries~
The research group consisting of the product R&D department of the chemicals division at Daikin Industries, Ltd. “senior engineer Dr. Shigeaki Yamazaki, Shinya Otani, Akinori Tani, and Nao Kobayashi” and assistant professor Dr. Yasuyuki Kondo and professor Yuki Yamada of the Institute of scientific and industrial research at The University of Osaka has proposed an approach that realizes a rational design based on numerical data, breaking away from the traditional trial-and-error method in the design of new electrolytes for lithium-ion batteries.
This finding is expected to contribute to higher voltages and enhanced safety for lithium-ion batteries, leading to innovations in various social infrastructures, including electric vehicles, renewable energy storage systems, and uninterruptible power supplies for data centers.
The research results were published in the international academic journal "Advanced Materials" (Impact Factor* 26.8) on October 25, 2025.
Summary of the announcement
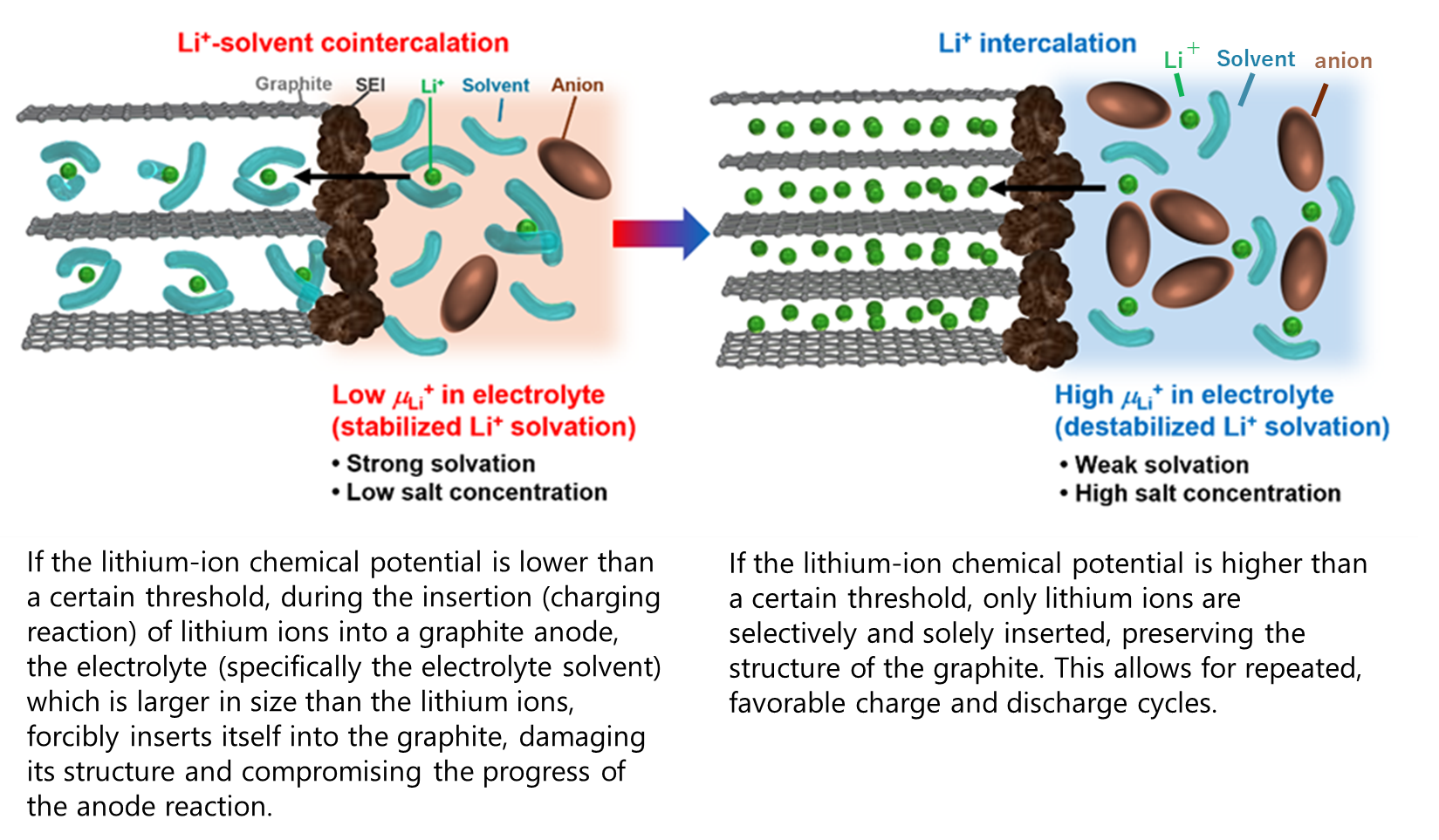
Lithium-ion batteries are essential to modern life, being used in smartphones, electric vehicles, and more, but further performance enhancements and safety improvements are required. Graphite has been widely used as an anode material in lithium-ion batteries, and in the development of new electrolytes, ensuring a good charge and discharge reaction with the graphite anode is an indispensable technological element. However, the quality of the charge and discharge reactions with graphite varies greatly depending on the type of electrolyte, requiring much time and cost to explore new electrolytes.
The joint research team addressed the above issues by discovering that the "lithium-ion chemical potential**" in the electrolyte, which indicates the stability of lithium ions, is a crucial index controlling the charge and discharge reactions of the graphite anode. To tackle these challenges they proposed a quantitative electrolyte development process based on numerical data.
Moreover, this new approach demonstrated that fluorinated ether solvents with specific structures enable good charge and
discharge with graphite anodes, showing promise as a candidate material for next-generation electrolytes.
This discovery contributes to the further expansion of applications and the high performance (high output, high voltage, high safety) of lithium-ion batteries.
Daikin Industries, Ltd. will continue to promote the development of advanced technologies through industry-academia collaboration to create new value.
Figure 1. Schematics of graphite negative electrode reactions in various electrolytes depending on electrolyte Li+ chemical potential.
Reference URL:SANKEN, the University of Osaka
>A new quantitative rule for designing better batteries
*Impact Factor: A metric evaluating the influence of a journal (academic journal), calculated from the frequency it is cited by other journals.
**Lithium-ion chemical potential: Refers to the partial molar Gibbs energy of lithium ions and indicates how stably lithium ions exist in a system (such as within an electrolyte). In an electrolyte, lithium ions are coordinated with organic solvent molecules and anions (solvation structure). The solvation structure influences the stability, i.e., chemical potential, of the lithium ions. For instance, the stronger the coordinating power of the organic solvent or anion, the lower the lithium-ion chemical potential.



