![]()
Under development material
08/2021 (04/2023 updated)
Automotive refrigerant R-474A (under development)
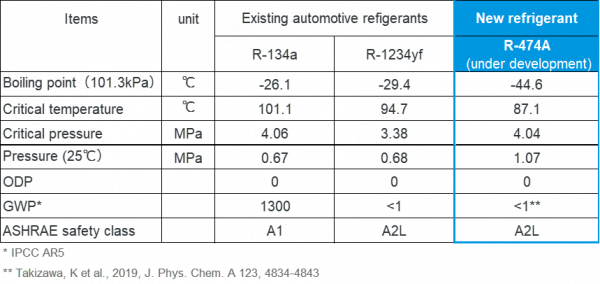
Daikin’s latest refrigerant with low environmental impacts R-474A (under development) is designed for automotive HVAC applications. It delivers increased cooling and heating capacity with superior efficiency. In particular it excels in delivering strong heating performance for an electric vehicle passenger cabin, where the exhaust heat from the combustion engine is not available, and the use of resistance heaters limits the vehicle’s range.
Background of development
Heat pumps are fast becoming the solution to improve the thermal performance of BEVs (Battery Electric Vehicles) and PHEVs (Plug-in Hybrid Electric Vehicles), thereby mitigating driving range loss in winter conditions. However, the refrigerant currently in use – R-1234yf – presents limitations as a working fluid in heat pump systems due to its low pressure and relatively high boiling point, which limits heating performance with low outside air temperature conditions. For this reason, electric heaters are sometimes required to support the heating of the vehicle cabin.
Our new refrigerant blend R-474A has a lower boiling point and higher pressure, providing improved capacity across the required temperature range.
Features
- Environmental Impact: GWP <1
- Safety: Mildly flammable, comparable to R-1234yf
- +40% additional heating and cooling capacity compared to current solutions
- Ability to heat at ambient temperature down to -30℃
- Matching efficiency (COP) to R-1234yf across all temperatures
- Manageable temperature glide (4K)
Table 1. Property comparison of refrigerants
Performance
An initial performance test using an existing Automobile AC compressor – a drop-in evaluation with compressor for R-1234yf – is shown below. As a result of evaluation under the test conditions shown in Table 2, R-474A has improved heating capacity compared to R-1234yf (Figure 1). Another test to provide the similar heating capacity has shown that heating efficiency is higher than R-1234yf.
Those evaluations show the potential higher heating capacity of this refrigerant when using in the system. Further tests will be done to understand the behavior of the refrigerant and optimized the MAC system to adapt its best use.
Table 2. Specification and test condition
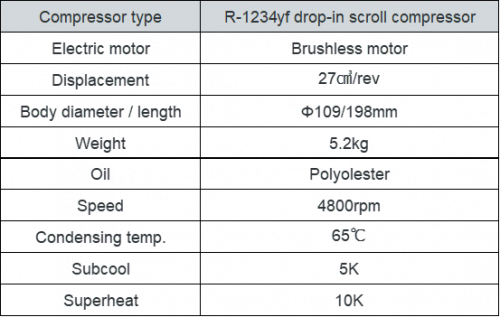
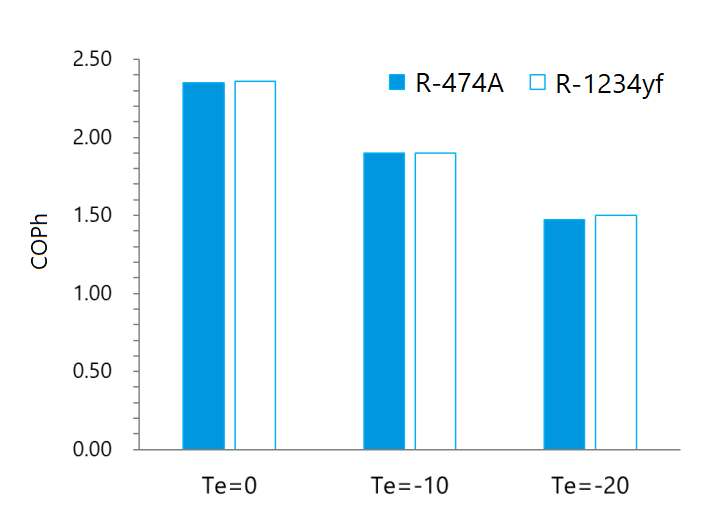
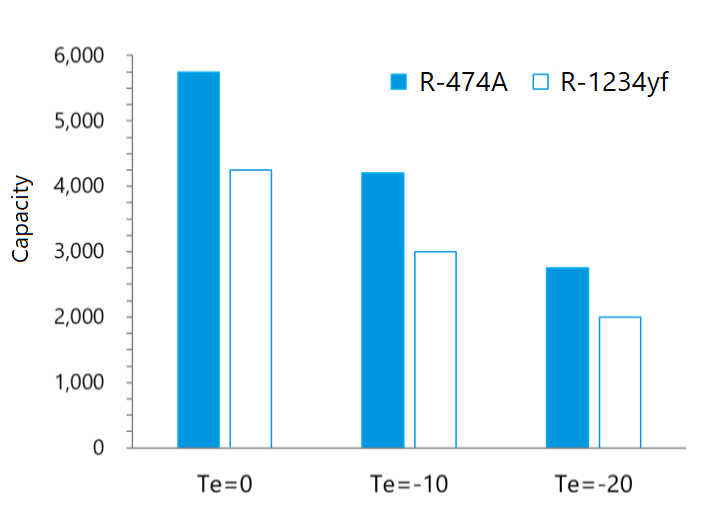
Fig.1. COPh and capacity in variable Te
Note(1) : The pressure / temperature are conditioned by the test rig so it does not represent the system performance including the heat transfer nor the pressure drop.
Note(2) : All the data shown in this report are not guaranteed.
RELATED ARTICLES





